

That’s because if you want to transpose a song from the key of C to D, you then need to raise the pitch not by one, but by 2 semitones!

In the example, notes C – C# and B – C is a semitone. Let’s take a look at two semitone examples: In Western music, notes are in a chromatic scale, running from the left, bass, to treble on the right.Ī semitone is the smallest interval between two notes. When you transpose the pitch of a song, you’re essentially bumping it up by semitones.įirst, picture a music keyboard. Sounds easy, yes?īut before we jump into our audio editing software and start pitching things – it’s important to learn a bit of music theory and how pitch-shifting effects work. To help give you some perspective, bird chirps have high frequencies usually ranging from 1000Hz to 8000Hz and therefore are perceived as a high pitch.Īn engine rumble, on the other hand, has a low frequency, below 400Hz, and is considered a low pitch sound.Īnd transposing simply means shifting a song or sample’s pitch. Sound (sound waves) are produced through vibrations and the frequencies of these vibrations are measured in hertz (Hz).
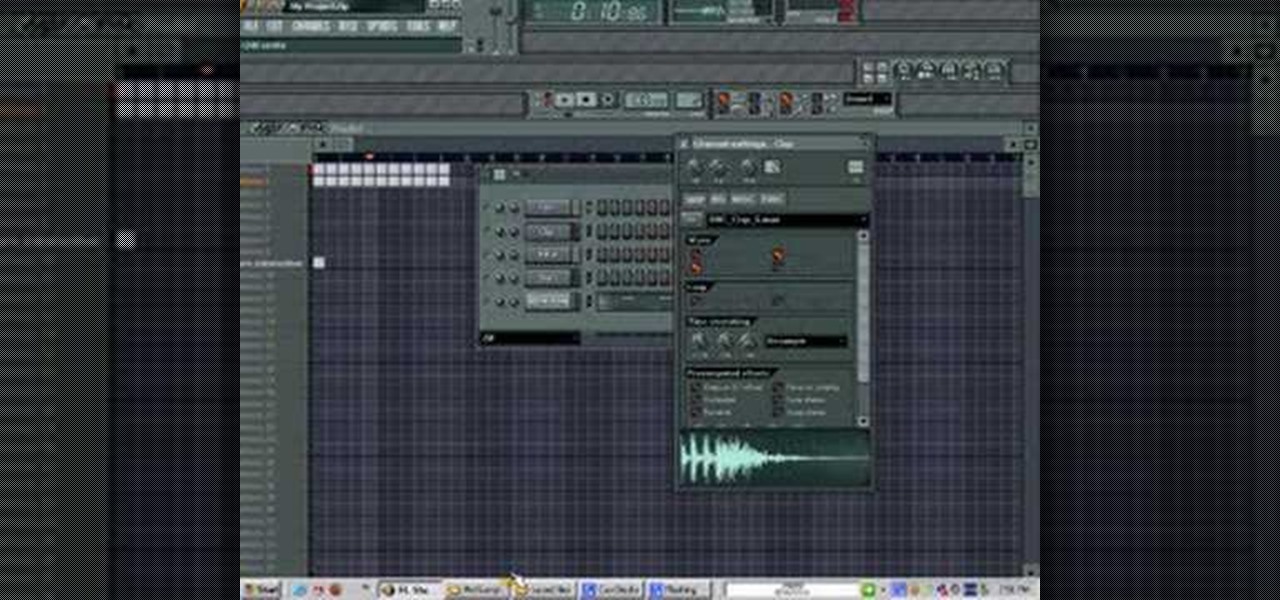
What is transposing & how does it work?īefore we go into the nitty-gritty of pitch shifting a song, it’s best to learn what a music pitch is in the first place.Ī pitch refers to the position (how high or low) of a sound. This is when pitch-shifting and transposition come in, to raise or lower the original pitch of a song or sample. The key of the sample does not fit with your track. You found a great sample, but there’s a slight issue. Perhaps you’re into music sampling and production. Have a song you want to sing along to, but the key is too high?


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
